Managing user login access to data resources, in order to reduce the risk of unauthorized access, is a significant challenge. There are clear benefits of having a robust password policy and a strong authentication process.
The best practices for a stronger login security policy include having the requirement for users to create complex passwords and change their passwords regularly. However, relying only on a single username and password, no matter how complex the password is, creates vulnerabilities if the login credentials are compromised.
Combining a multi-factor authentication process with a strict password policy is more secure.
What is multi-factor authentication?
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) helps secure a digital identity as part of an organization’s identity access management efforts according to its security policies. MFA requires two or more identification credentials to gain access to a protected system.
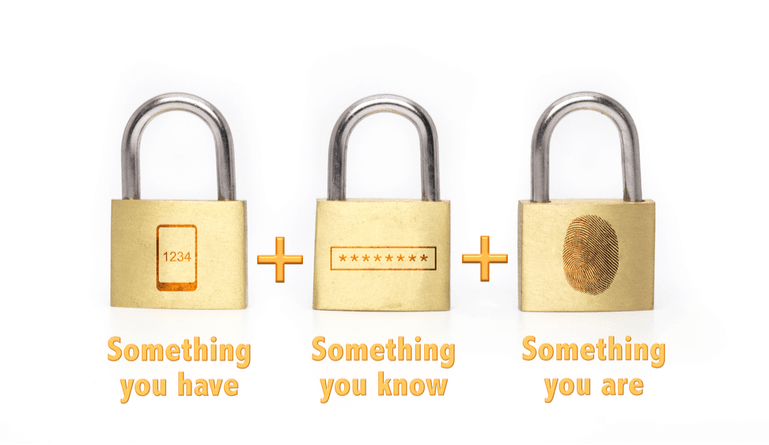
Identification credentials come from three categories, which are:
- Knowledge: These are things that a user knows, such as a password or answers to challenge questions.
- Possession: These are things that a user has, such as a physical photo-ID card, a mobile phone, a physical key, a digital encryption key, a hardware USB dongle (like a key fob), or a digital security token.
- Physical Characteristics: This is biometric data that includes such things as fingerprints, facial recognition, bone density, retinal/iris scans, and DNA.
Secure authentication of users is improved by requiring two or more of these independent credentials for system access.
Practical MFA Solutions
MFA existed well before computer systems came into being. An example of this is having to present an identification card to a security guard and tell the guard the correct password to enter.
Contemporary examples of practical MFA solutions are:
- Having to swipe a card and then enter a PIN.
- Using a username and password on a protected website to login and having to enter a one-time-use code sent as an SMS text message to a mobile phone or as an email.
- Scanning a fingerprint and answering a security question.
- Downloading a VPN app with a valid digital certificate and logging on with a username and password using the app.
- Using a USB hardware dongle connected to a computer to get a one-time code that is then used with a username and a password to log in with a downloaded VPN app.
Why is there a need for multi-factor authentication?
TechBeacon gives many reasons why using MFA is important, which include
- Security breaches caused by hackers stealing passwords are 95% of all cyber-attacks.
- Identity theft is increasing because it is a low-risk/high-reward crime, especially for criminals located outside a legal jurisdiction.
- Cyber-attacks are not limited to large companies. About 31% of hacking attacks are made on companies with 250 or fewer employees.
- The anonymity of cryptocurrencies increases ransomware cryptocurrency demands in malware attacks.
- Network-side IT security, such as anti-virus software, firewalls, malware detection, vulnerability testing, intrusion blocking, and other network monitoring is useless against a holder of valid but stolen, credentials. A login seems authentic if the credentials are not known to be stolen.
- A hacker may go undetected for years when the hacker’s login is made using stolen credentials. Incorporate espionage, valuable information that creates a competitive advantage may be compromised without anyone being aware this is happening.
MFA Authentication and Web SSO
Web single sign-on (Web SSO) is a centralized web-based service that authenticates a user for may web services after the user signs in with a singer username and password. Web SSO replaces all the other usernames and passwords for many disparate systems with a single login.
MFA multi-factor authentication works well with web SSO to increase security by requiring extra steps for the login to the web SSO system. Since a web SSO service grants access to possibly many web services, it is highly recommended to use MFA for improved security.
Microsoft Multi-Factor Authentication
Microsoft multi-factor authentication uses a two-step process. The first step is to start the login with a username/password combination. Then, a security code is sent to a trusted device such as a known user’s mobile phone, email account, or an authenticator app for the second step of the authentication.
If the login attempt is from a new device that is not yet known to Microsoft, the user must answer additional security questions correctly as well.
Microsoft recommends having a minimum of three security checks for each account. If a password is lost or forgotten, Microsoft still requires two independent authentications to grant access if MFA has been enabled. A password alone is not enough to gain access.
With only the password, it may take up to one month to gain access by going through Microsoft customer service and there is a chance that the account will be permanently inaccessible.
Multi-Factor Authentication Security Risks
MFA includes two-factor authentication, which improves security over using a single password for access; however, hacking two-factor authentication is possible.
Here are some ways that authentication can be breached:
- Bypass: Just because authentication is used does not mean that it cannot be bypassed by cyber-attacks on software vulnerabilities and exploits.
- Phishing: Hackers use a fake website that is an identical copy of the real one to steal the generated credentials that are entered by the user who is not aware the entry is being made on a fake website.
- Token Stealing: After authentication is made, the authentication system sends an authorized user a digital token that is used by the user’s browser to gain access to protected web services. Every use of this token on the web creates a vulnerability where it can be stolen.
- Malicious Software: Malware that finds its way onto a computer can hide and wait for a user to use an authentication process to access a protected web service such as a bank account. After the malware captures the authentication token, it runs hidden login sessions in the background.
- Updated ‘One-Time’ Codes: This is a way to hack one-time-use security codes that are updated by an algorithm based on a time-sync calculation. The devices that generate the one-time codes constantly update them based on a timing calculation. Hackers who discover the time-sync algorithm pattern or steal it can recreate any one-time-key codes if they start with one.
- Stolen Biometrics: Biometrics are attractive to use for security because they are unique to a person. However, this uniqueness creates a counter-intuitive risk. If the biometric data is stolen, it can be used to fake a person’s identity any time thereafter. A person can change a password but not easily change their fingerprints. To steal fingerprints, the real fingers are not needed, only the data collected by a fingerprint scanning device that is compromised.
Other Benefits and Solutions of MFA Authentication
1. Zero-Trust Policy
A zero-trust policy assumes that every login attempt is not trusted. MFA is a vital part of this process because the added authentication increases the probability that the person attempting a login is the person who is authorized to do so. The strongest authentication applications of MFA require three or more independent security verifications.
2. MFA and Regulatory Compliance
PCI (for payment card transactions) and HIPAA (for medical records) regulations require MFA to secure those systems for legal compliance.
3. Meeting NIST Level of Assurance Standards
The National Institute of Standards (NIST), a division of the U.S. Department of Commerce, has Level of Assurance (LoA) standards that require the use of MFA. The NIST SP 800-63 standards are the technical requirements for authentication systems used for electronic commerce and government operations in the United States.
Artificial Intelligence and MFA
Artificial intelligence (AI) programming is now being used extensively in the financial systems. Data mining of Big Data creates analytics that uncovers suspicious-activity patterns. AI is used to improve authentication algorithms through machine learning. These systems predict unauthorized access and block fraudulent transactions.
KMPG reports that these efforts, combined with MFA, are now succeeding in blocking about $17 billion in unauthorized transactions for bank account holders each year.
Conclusion
MFA is part of a comprehensive strategy to improve security with more robust authentication methods. Organizations should require employees to use it. Individual users, when given the option to use MFA, should take advantage of the added protection MFA provides.