In this day and age, data security is probably one of the biggest concerns for any business. All businesses have a ton of data at their disposal – transactions, knowledge, communications, consumer data, infrastructure details, etc. For all businesses, it is beyond important to ensure maximum security for all of its data.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication?
Multi-Factor Authentication is an effective way to add another layer of enhanced security to your devices and infrastructure. It makes use of multiple credentials for identity and access management. For instance, instead of simply asking for a biometric scan and a password, it may also ask you for a code, or another biometric scan.
The reason Multi-Factor Authentication is opted for is because traditional usernames and passwords are vulnerable to breaches and hacks. Thus, creates multiple layers of security, thus thwarting hacking attempts.
How does Multi-Factor Authentication work?
To begin to understand how MFA works, it is important to first note that there are two types:
- Device Multi-Factor Authentication: An authentication process that implements the process directly at the point of login to a system.
- Application Multi-Factor Authentication: An authentication process that implements the process upon attempting to gain access to one or more applications
The process, however, is the same in both the cases. When you try to access any particular file, folder, application or device, the authentication system will ask for the factors one by one to validate your ID. Once you’ve proven your ID to the system, you are then granted access.
How secure is Multi-Factor Authentication?
MFA is good at identifying login attempts that are out of the ordinary and flags them. In such a situation, this adaptive technology may tighten security by requesting additional credentials. Therefore, while the authentication process isn’t exactly Pentagon secure, it does ensure breaching or hacking attempts are flagged and blocked as far as possible. It has evolved as the single most effective control to insulate an organization against remote attacks
Importance of Multi-Factor Authentication
MFA is essential for your organization. Here are a few reasons why:
- Identity theft is a growing threat – Identity theft is a rather common, easy, low-risk, high-reward type of crime and a major threat to all businesses. Password theft is constantly evolving as hackers employ methods like keylogging, phishing, and pharming. Therefore, it is a must in these times.
- Your anti-virus just isn’t enough – Anti-virus systems and advanced firewalls are necessary security elements, as are vulnerability tests. Without authentication, though, your system is susceptible to intruders.
- They won’t just take your data – Cyber criminals do more than merely steal data. Often they destroy data, change programs or services, or use servers to transmit propaganda, spam, or malicious code. MFA helps prevent all of these.
- Multi-Factor Authentication is already ubiquitous – People are accustomed to authentication procedures in their personal as well as professional lives. Social media, banking, gaming, and email platforms have all rapidly adopted MFA. Bringing it into your workplace is no longer an option, but a basic security measure.
(Also Read: Benefits and Solutions of Multi-Factor Authentication)
Types of Multi-Factor Authentication Factors
Generally, MFA works by requiring two or more of the following authentication factors:
- Something you know – this could be either a password, a pin or a code that you set up for the system.
- Something you have – this could be either a QR code to scan on an ID or badge, or maybe even an OTP sent to your mobile number or email address.
- Something you inherited – this could include any form of biometric authentication such as a facial scan, fingerprint scan or even a retina scan.
- Somewhere you are – this could be either to a specific computing network or utilizing a GPS signal to identify the location.
In order to access the desired file or folder, you will have to provide the aforesaid credentials one by one to prove to verify their identity to the system.
When to use Multi-Factor Authentication?
As a business, it is important to know if you do require MFA or not.
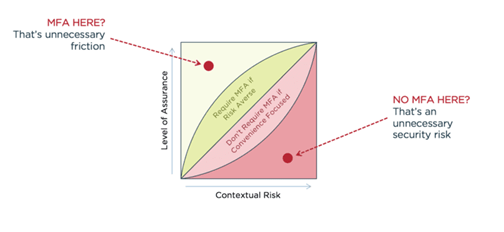
SOURCE: Pingidentity
Pingidentity(1) shows the graph that will help you decide whether or not you should implement it or not. For starters, it is important to understand that you may not need MFA throughout your entire organization. For example, entry level employees and interns may not need Multi-Factor Authentication since they would just have viewing access to your data such as sales, transaction, customer profiles etc. Higher level management and employees, on the other hand, should definitely be given it as they are the ones who would most likely edit the data for projection and strategy purposes.
(Also Read: Multi-Factor Authentication: How and Why You Should Protect)
Pros and Cons of using Multi-Factor Authentication
The Pros are as follows:
- Protects sensitive information: Your company would most likely be holding a lot private and sensitive user data such as phone numbers, addresses, payment option details for consumers as well as employees. Deploying a Multi-Factor Authentication system ensures that all of this data is safe guarded.
- Extremely secure: If a hacker has somehow acquired a user’s password to a system, they cannot gain access unless they have the token (which is in the user’s possession), and obviously the biometric scans. Thus, it is extremely secure.
- Lost devices? Not a problem: Without MFA, a lost, stolen or misplaced device could create havoc in the IT department. Device-based Multi-Factor Authentication ensures that lost devices don’t mean that your information is compromised.
The Cons are as follows:
- Blocked access: If you haven’t set up backup resources for authenticating user access, you cannot be granted access to a particular application or system. So a lost possession, injured finger (for biometric) would mean you would have to immediately run to the IT guys lest your login attempt be flagged.
- Can be expensive: MFA can be quite expensive if an organization uses a solution that requires installation of on-premise hardware and has to integrate it with existing identity solutions.
- Time-consuming:The time needed to log in on your system and verify using a mobile device can be inconvenient, especially if you’re in a rush.
Difference between Multi-Factor Authentication and Two-Factor Authentication
There is but one difference between MFA and 2FA – the number layers of security.
Two-Factor Authentication always employs two of the different factors to verify the user’s identity. Multi-Factor Authentication, on the other hand, could involve two or more of the factors. “Multi-Factor” just means any number of factors greater than one. An adaptive Multi-Factor Authentication system would add security layers until the login attempt does not seem suspicious.
Applications and Providers of Multi-Factor Authentication
There are mainly 4 applications of Multi-Factor Authentication systems:
- Time-based One-Time Password (TOTP) – When you’re logging in to access a particular file or folder and the application or device is TOTP protected, then it send an OTP, or a one-time password, to your mobile number which would only be valid for a specific time period, say 10 minutes.
- Short Message Service (SMS) – SMS verification works by asking the user to enter a particular mobile number upon login attempt. The system then sends an SMS to said number. If the SMS is delivered and instructions completed, access is granted.
- Electronic Mail (Email) – Email verification is another common application of MFA, wherein user identity is verified by sending an email with a redirect link.
- Push Notifications – If a login attempt is made on another device, the user is prompted with a push notification on the original device and access is granted from there.
The best providers of Multi-Factor Authentication systems are:
- Duo Security
Duo Security’s(2) frictionless Trusted Access platform protects users, data and applications from malicious hackers and data breaches. It addresses security threats before they become a problem by verifying the identity of users and the health of their devices.
- Google Authenticator
Google Authenticator(3) implements a two-step verification service along with a Time-based One-time Password Algorithm and HMAC-based One-time Password algorithm, for authenticating users of software applications.
- LastPass
LastPass(4) provides simple control and unified visibility across every entry point to your business from single sign-on (SSO) and password management to adaptive multifactor authentication (MFA). LastPass Identity gives superior control to IT teams.
- Ping Identity
Ping Identity(5) builds identity security for the global enterprise with an intelligent identity platform that offers comprehensive capabilities including single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), directory and more.
- Auth0
Auth0(6) provides the simplicity, extensibility, and expertise to scale and protect identities in any application by making use of Multi-Factor Authentication systems.
Frequently Asked Questions about Multi-Factor Authentication
Q. Is username and password Multi-Factor Authentication?
A. It is an authentication method in which a computer user is granted access only after successfully presenting two or more pieces of evidence to an authentication mechanism: knowledge, possession, and inherence. Therefore, a simple username and password is not MFA.
Q. How to defend against Multi-Factor Authentication attacks?
A. It is very easy for hackers to breakthrough a Two-Factor Authentication system. Multi-Factor Authentication attacks are rare as it is difficult for hackers to obtain all three factors. Companies must, however, train their employees to identify phishing emails and be vary from them.
Q. How to add Multi-Factor Authentication?
A. Enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA) on your account will require an additional identity verification step at the time you log in. Once configured and enabled for an account, our system will require the use of an authentication code generated by an authenticator application each time you log in to your account. Users can set this up for themselves, or as an alternative, admins may set this up for each user.
Final Thoughts
Multi-factor authentication allows for a flexible and manageable way to balance the overall customer experience with modern security requirements. Your login process, access to sensitive information, and security are of topmost concern for many companies, employees, and customers. Taking care of these matters show you care and are taking extra precautions and measures to defend your systems.